Early detection of unknown inflammation and nosocomial infection processes is crucial nowadays for patient’s survival. In this respect, clinical practice is taken profit of molecular imaging technologies to diagnose these pathologies in early stages. But in many cases correlation between imaging findings and patient evolution is still undetermined. Animal models are indispensable for the study of key issues in disease pathophysiology, for testing promising new treatments and also for find imaging markers of disease progression.
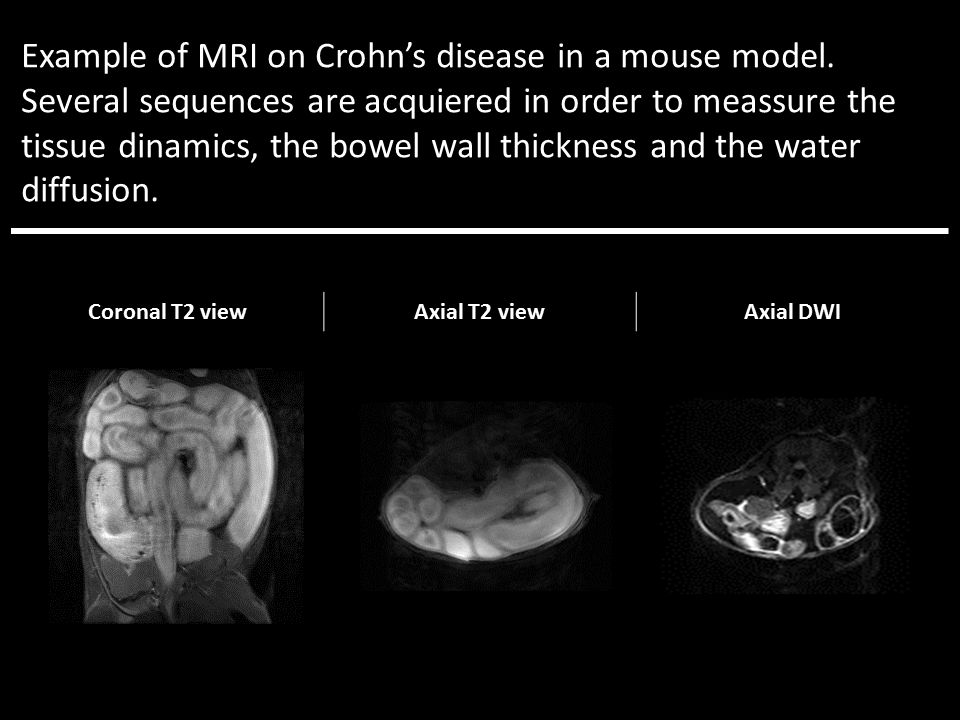
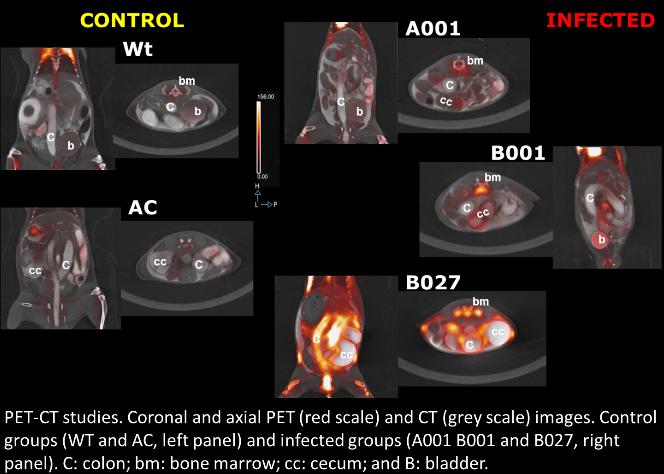
Nosocomial infection is a hospital-acquired infection whose development is favored by a hospital environment. Most common nosocomial infections are catheter-related or antibiotic-related infections. Candida spp., Staphylococci and Staphylococcus aureus are the principal microorganism involved on catheter-related infections whose can induce endocarditis or pneumonia. On the other hand, antibiotics destroy normal flora of our organism promoting opportunistic microorganism appearance such as Clostridium difficile, provoking colitis. Crohn disease also produces colon inflammation but it is caused by a combination of environmental, immune and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. Signs and symptoms are varied but Crohn patient are at greater risk of bowel cancer. In this context our group is taking profit of biomedical small animal dedicated techniques to look for imaging markers in order to foresee the disease progression on different rodent models.
Also our group is developing new imaging agents, particularly at improving specific targeting interactions, efficiently overcoming biological barriers, and providing agents that are useful for more than one imaging modality. In this particular, we are designing new radiotracers for target specifically Gram possitive (see Molecular Imaging Probe).
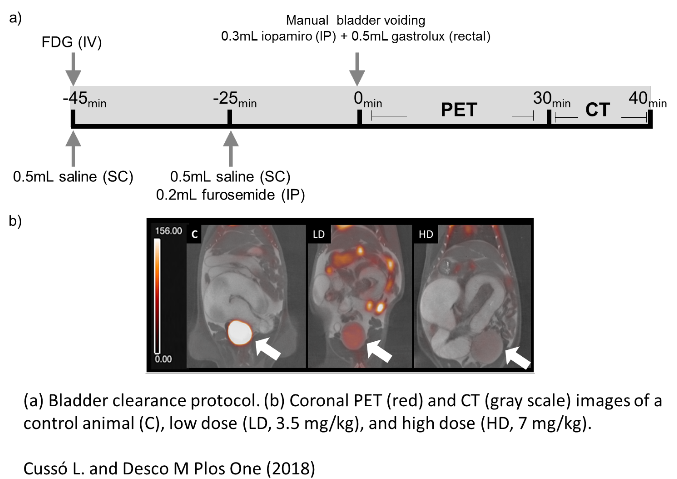
Although the importance of FDG in the clinical routine remains unquestionable, there are well-known detectability problems in several applications due to its non-specific tissue uptake.We characterized a non-invasive and effective pre-imaging protocol that reduces accumulation of FDG in urine. Our pre-imaging protocol is based on the combination of hyperhydration and furosemide during the FDGuptake period.
Selected Articles
- Cussó L, Reigadas E, Muñoz P, Desco M, Bouza E. Evaluation of Clostridium difficile infection with PET-CT image in a mouse model (in press)
- Cussó L, Desco M. Suppression of 18F-FDG signal in the bladder on small animal PET-CT. PLOS ONE 13(10): e0205610, 2018
- Salinas B, Guembe M, Cussó L, Kestler M, Guinea J, Desco M, Muñóz P, Bouza E. Assessment of the Anti-Biofilm Effect of Micafungin in an Animal Model of Catheter-Related Candidemia. Medical Mycology, 2018
Funded Grants
Salinas, B. and Desco M (2017-2019) Diagnóstico de la bacteriemia por Gram positivos mediante nuevos trazadores PET selectivos. PI16/02037. Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
Fernández Avilés F. (2017-2019) . The microbiome as a target for precision medicine. A frontier exploration from established to innovative indications. PIE16/00055 Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
Bouza, E. (2014-2016). Evolución de la Prevalencia, Diagnóstico, Caracterización Fenotípica y Genotípica de la Infección por C. difficile (ICD) en España. Factores de Riesgo de Recurrencia y Valor del PET-TAC en la ICD. PI13/00687. Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad.
Muñoz, P. (2014-2016). Proyecto PROMULGA II: Validación de la eficacia de un "bundle" de medidas en la incidencia, diagnóstico rápido, tratamiento y mortalidad de la infección fúngica nosocomial. PI13/01148. Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad.
Menchen, L. (2014-2016). Disfunción de barrera, fibrosis y carcinogénesis asociadas a inflamación crónica en un modelo murino de enterocolitis: análisis mediante imagen y evaluación de un nuevo marcador molecular. PI13/02555. Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
Vaquero, JJ. (2012-2017). Model-based preclinical development of anti-tuberculosis drug combinations (PreDiCT-TB). 115337. FP7-IMI - Seventh Framework Programme (EC-EFPIA). European Union
 Related Research Lines
Related Research Lines
Preclinic Research
Molecular Imaging Probe Beatriz Salinas
Technological Development
PET technologies Juan José Vaquero
Imagen por Rayos X Mónica Abella




Idiomas