Setting up a C-arm for its use as a tomograph.
The work included in this thesis is framed on one of the lines of research carried out by the Biomedical Imaging and Instrumentation group from the Bioengineering and Aerospace Department of Universidad Carlos III de Madrid working jointly with the Gregorio Marañón Hospital. Its goal is to design and develop a new generation of Radiology Systems, valid for clinical and veterinary applications, through the research and development of innovative technologies in advanced image processing oriented to increase image quality, to reduce dose and to incorporate tomography capabilities. The latter will allow bringing tomography to situations in which a CT system is not allowable, due to cost issues or when the patient cannot be moved (for instance, during surgery or ICU). It may also be relevant to reduce the radiation dose delivered to the patient, if we can obtain a tomographic image from fewer projections than using a CT.
In that context, this thesis deals with incorporating tomography capabilities in a system originally design for planar images: the SIREMOBIL C-arm developed by SIEMENS. The system consists of an X-ray generator and a detector mounted in an arc-shaped wheeled base that allows a great variety of movements.
The use of this C-arm for tomography presents several difficulties: (1) the detector is an image intensifier which is an analog detector with image distortions, (2) the system may have mechanical strains changing the relative positions of the source and detector, and (3) the movements of source-detector pair may differ from a circular path. To obtain good quality images, it is necessary to design a new acquisition protocol that solves the effects of these non-idealities including an exhaustive calibration of the system, not needed when it is used for planar imaging.
First a calibration algorithm has been adapted to the system under study. Besides the mechanical calibration of the source and detector relative positions, it is necessary to obtain the angular position of the complete system. This work presents the effects of errors in the angle estimation and describes the implementation of a positioning system that obtains the angular position with the required precision for a tomographic reconstruction. A digital detector has also been incorporated to the system to solve the drawbacks of the image intensifier together with the development of a software tool to transform the data acquired into in the appropriate format for the reconstruction software.
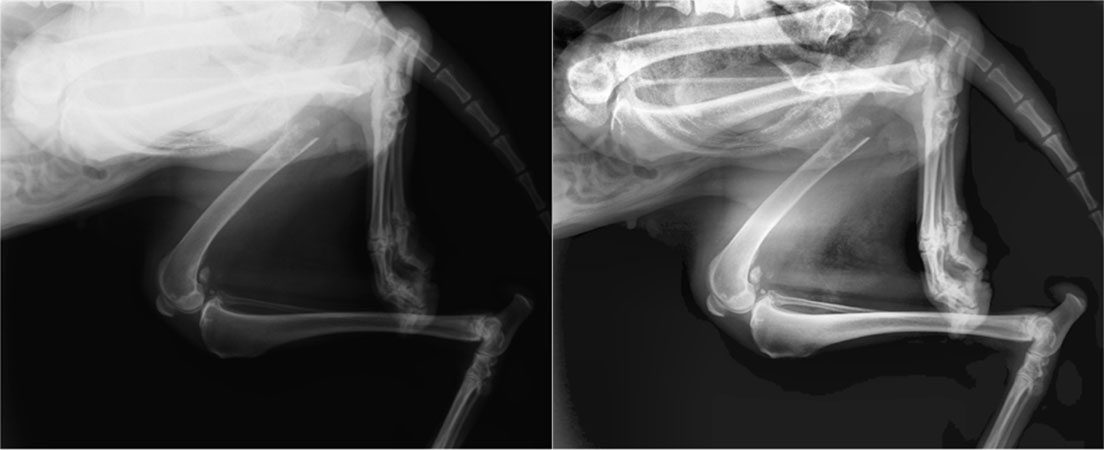
Evaluation of the proposed acquisition protocol on phantoms and rodent data show the feasibility of the proposal.
Part of this project has generated a scientific publication and was presented as an oral communication at the Congreso Anual de la Sociedad Española de Ingeniería Biomédica (CASEIB). Finally, it should be noted that the work of this thesis has a clear application in industry, since it is part of a proof of concept of the new generation of Carm systems which will be commercialized worldwide by the company SEDECAL.
Idiomas